MUSCULATURE
In cnidaria, muscles in the epidermis are usually longitudinal while those in the gastrodermis are usually circular (Ruppert et al., 2004). Both layers of muscle are smooth (Ruppert et al., 2004). The main medusae muscle is the oval-shaped coronal muscle (Ruppert et al., 2004) as seen in the figure below.
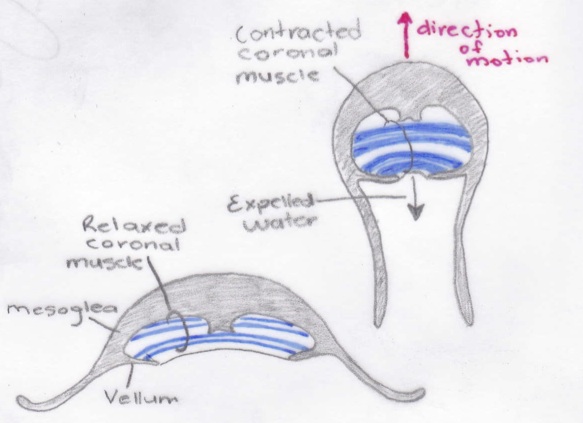
Figure 5.3: Longitudinal coronal muscles in a
medusae. Adapted from Ruppert et al., 2004. |
Medusa muscles are used in locomotion, circulation, food capture, bioluminescence and reproduction (Ruppert et al., 2004).
For further information, jump to:Respiration, Circulation & Excretion or Locomotion. |